Problem1 - e¶
Discuss the computational time for different methods. Examine how the computational time depends on the grid resolution and evaluate the temporal complexity of the methods.
Euler equation (Pure convection problem)¶
In this test, only a part of Euler-Explicit cases was employed for analysis because the method was unstable beyond certain value of Courant number.
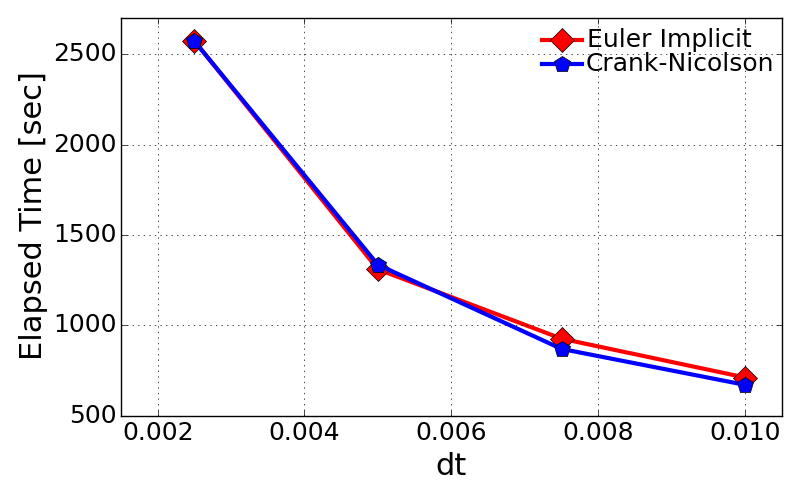
- Computational time with different time step, dt
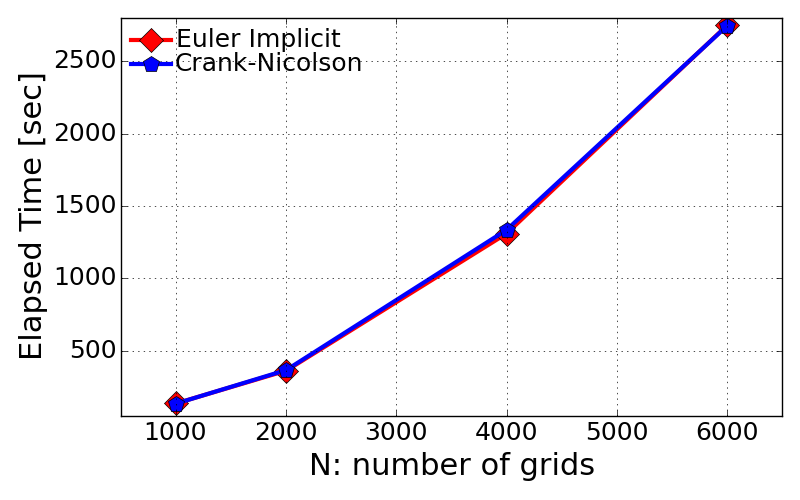
- The evaluation of computational time was done for single case of grid size, N = 4001.
- Both Euler implicit and Crank-Nicolson methods show almost equivalent levels of computational time.
- The computational time is dramatically dropping with increase of time step. This is quite natural phenomena because the bigger time increment will jump up to the targeted solution in time.
- Computational time with different grid resolution
Burger’s equation (Convection + Diffusion)¶
In this test, all the conditions of Euler-Explicit cases were employed for time consumption analysis regardless of instability of numerical solution. Even if instability happens in the solution, the computational time can be evaluated because the simulation was running without stopping. In that case, accuracy of simulation cannot be assessed as observed in the previous section.
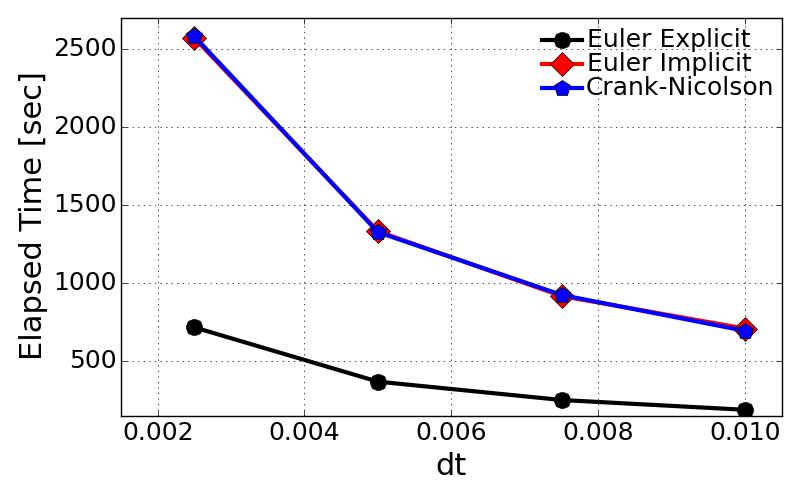
- Computational time with different time step, dt
- The evaluation of computational time was done for single case of grid size, N = 4001.
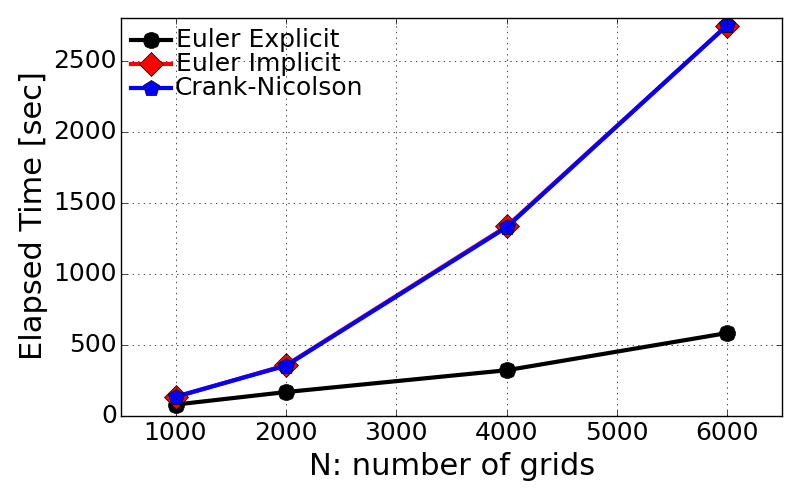
- Most interestingly, Euler explicit is quite efficient in computational time consumption.
- In contrary to both implicit schemes, explicit scheme will not need to construct matrix.
- Also it does NOT necessarily conduct any vector calculus which would basically require higher consumption of CPU time and memory storage.
- Computational time with different grid resolution